[ad_1]
In the 5G era, there are some new terms that need explanation. The 5G network is more advanced and complex than its predecessor, his 4G. One term that needs explanation is “5G dual connectivity.” His previous 4G network is far from perfect. As such, 5G required many upgrades. To solve the 4G coverage and capacity problem, the new generation network will bring “5G dual connection”. 5G dual connectivity means that your smartphone can connect to his two base stations at the same time. These two base stations can be both 4G base stations and his 5G base stations. But it can also be two 5G base stations. Therefore, it is also called MR-DC (Multi-Radio Dual Connectivity) or NR-DC.
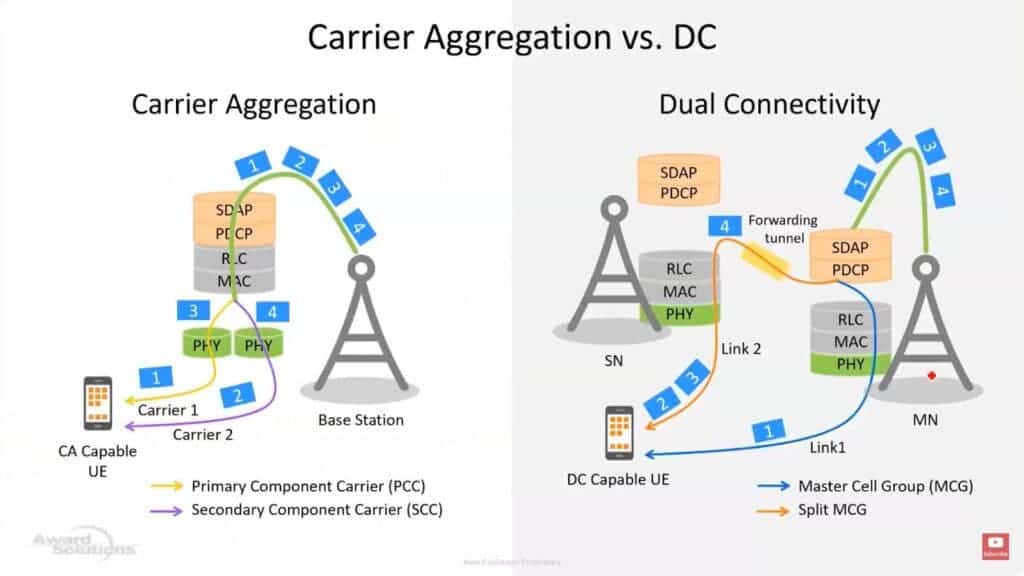
The architecture doesn’t seem complicated. However, there are some issues. Are there primary and secondary points between these two base stations? Can dual connectivity and carrier aggregation coexist? In which base station is the control plane? How to split user plane data? Do you have any requirements? These are multiple questions that need answers.
First, these two base stations serve users, but there are primary and secondary points. There is a master node (or MN node) with high status. I also have a secondary node (SN node) with a low status. The master node is also the primary node. When a smartphone needs his 5G connection, it connects to the primary node first. Then add a secondary node. The master or primary node is also the “anchor point” and interacts with the core network control plane.
MCG vs SCG
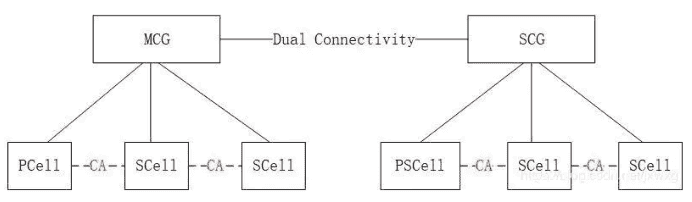
It supports multiple carriers internally for carrier aggregation regardless of whether it is a primary or secondary node. For the master node, when internal carriers are aggregated, it is equivalent to grouping multiple carriers together. Collectively, this group is called the Master Cell Group (MCG). Similarly, multiple cells within a secondary node are called a secondary cell group (SCG).
Giztina news of the week
In MCG, primary cells are also called Pcells, similar to common carrier aggregation. A secondary cell is also called a Scell. For SCG, the primary cell he called PSCell (Primary Secondary cell). The rest of the normal secondary cells are still called secondary cells SCell. Primary cells, whether MCG or SCG, are undoubtedly very important. Therefore, PCell and PSCell are collectively called Special Cell (or spCell for short).
The data bearer between mobile phone and master node is the MCG bearer. Similarly, the data bearer between the mobile phone and the secondary node is the SCG bearer. If a mobile phone has a primary node and a secondary node bearer at the same time, it is a split bearer. This indicates that the data is split at certain nodes. The base station connects to your smartphone and core network at the same time. This means that the field of view is much wider than that of smartphones. When the smartphone receives the data, it knows the originating node.
Complexities of 5G dual connectivity
As mentioned earlier, smartphones can connect to 4G and 5G networks at the same time. However, determining whether the connection is his 4G core network or 5G core network is complicated. Also, it is not an easy task to determine whether a base station is a 4G base station or a 5G base station. To describe this, we can use non-standalone (NSA) and standalone (SA) networks. Using option 3x of NSA architecture and option 2 of SA architecture as an example, we will see how both implement his 5G dual connectivity.
5G NSA Option 3x
Option 3x is basically a 5G dual connection between a 4G base station and a 5G base station. This is also called EN-DC. The core network adopts 4G EPC, and the 4G base station is the main node. This is the anchor point for the control plane. In such scenarios, 5G base stations become secondary nodes. Secondary nodes are also distributed control points for the user plane.
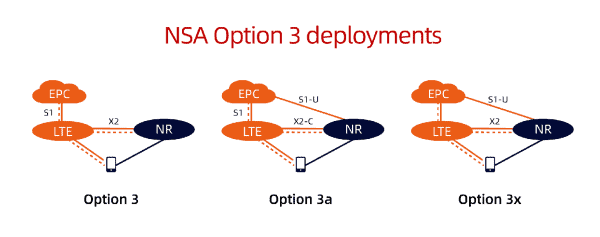
For voice services, option 3x can only use 4G without offload. This forms an MN terminated MCG bearer. For data services, if the 5G base station does not perform offloading, it is the SN terminated SCG bearer.
Option 2
Implementing 5G dual connectivity with Option 2 is called NR-DC. This is a dual connection between 5G base station and 5G base station. The core network uses 5GC and one 5G base station uses Sub6G frequency band as main node and offload control point. The other 5G base station uses the mmWave frequency band as a secondary node. Deepening 5G deployments based on mid-band 3.5GHz or 2.6GHz independent networks (option 2), superimposing mmWave over NR-DC for ultra-fast uplink and downlink rates , more carriers choose this. Option for 5G dual connectivity.
Conclusion
A good portion of the details in this article are technical notes that the average smartphone user won’t understand. The bottom line, however, is that 5G dual connectivity means that your smartphone can connect to his two base stations at the same time. This ensures that your smartphone is always connected to the internet. Data is available from any network.
[ad_2]
Source link

