[ad_1]

Microsoft encourages customers to keep their Exchange servers up-to-date and take steps to harden their environment, such as enabling Windows Extended Protection and configuring certificate-based signing of PowerShell serialization payloads. I’m looking for
“Attackers trying to exploit unpatched Exchange servers are not going away,” the tech giant’s Exchange team said in a post. “An unpatched on-premises Exchange environment has too many facets of value to bad actors looking to steal data or perform other malicious actions.”
Microsoft also stressed that the mitigations it has announced are only temporary solutions and may “be insufficient to protect against all variations of attacks,” and users should protect their servers. You must install the necessary security updates for
Exchange Server has proven to be a profitable attack vector in recent years, with many security flaws in the software being weaponized as zero-days to hack into the system.
In the last two years alone, several series of vulnerabilities have been discovered in Exchange Server. This includes ProxyLogon, ProxyOracle, ProxyShell, ProxyToken, ProxyNotShell, and the ProxyNotShell mitigation bypass known as OWASSRF. Some of them are widely exploited in the wild.
Bitdefender described Exchange as an “ideal target” in a technical advisory published this week, while documenting several real-world attacks involving the ProxyNotShell / OWASSRF exploit chain since late November 2022. I’m here.
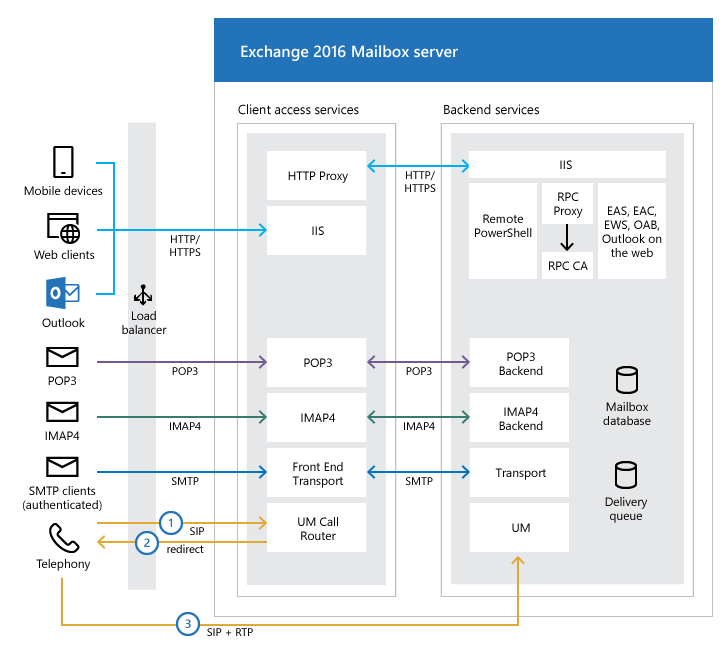
“We have a complex network of front-end and back-end services. [in Exchange], uses legacy code to provide backward compatibility,” said Martin Zugec of Bitdefender. “The backend service trusts requests from the frontend. [Client Access Services] layer. “
Another reason is the fact that several backend services run as Exchange Server itself and come with SYSTEM permissions. An exploit could grant an attacker malicious access to a remote PowerShell service, effectively opening the door to malicious command execution.
As such, attacks armed with the ProxyNotShell and OWASSRF flaws target the arts and entertainment, consulting, legal, manufacturing, real estate, and wholesale industries in Austria, Kuwait, Poland, Turkey, and the United States.
“These types of Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF) attacks allow attackers to send crafted requests from a vulnerable server to other servers to access resources or information that would otherwise not be directly accessible. ,” said the Romanian cybersecurity company.
Most of the attacks are said to be opportunistic rather than focused and targeted. Infections have culminated in attempts to deploy web shells and remote monitoring and management (RMM) software such as ConnectWise Control and GoTo Resolve.
Web shells not only provide a persistent remote access mechanism, but also enable criminals to carry out a variety of follow-on activities and even sell access to other hacker groups for profit.
In some cases, the staging servers used to host the payload were compromised by the Microsoft Exchange servers themselves, suggesting that the same techniques may have been applied to scale up the attack. .
We also observed an unsuccessful attempt by the attackers to download Cobalt Strike, a Go-based implant codenamed GoBackClient with the ability to gather system information and spawn a reverse shell.
Exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange is also a recurring tactic by UNC2596 (aka Tropical Scorpius), the operator of the Cuba (aka COLDDRAW) ransomware, in one attack leveraging the ProxyNotShell exploit sequence to access the BUGHATCH downloader. dropped the
“Initial infection vectors continue to evolve, with attackers eager to capitalize on new opportunities, but post-exploitation activity is well known,” said Zugec. “The best protection against modern cyberattacks is a defense-in-depth architecture.”
[ad_2]
Source link

