[ad_1]
Analyst organization Gartner has released its annual Magic Quadrant evaluating the world’s leading cloud infrastructure and platform service providers. In 2022, Oracle and Huawei made big moves.
Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud maintain their position as the only three clouds in the summoned quadrilateral valuable leader box.
But Oracle jumped out of the niche box and became a visionary, and Huawei debuted as a niche player.
Gartner Controversial Chinese Company Emerges Despite Concerns International Sanctions Hit Business, Poor PaaS Offerings and Poor Partner Ecosystem Did. On the positive side, Huawei Cloud is very strong in China and increasingly strong in Latin America, Southeast Asia and Africa. Huawei also has the advantage of extensive experience on-premises and in the cloud. Many of our carrier customers appreciate what it takes to work with demanding customers.
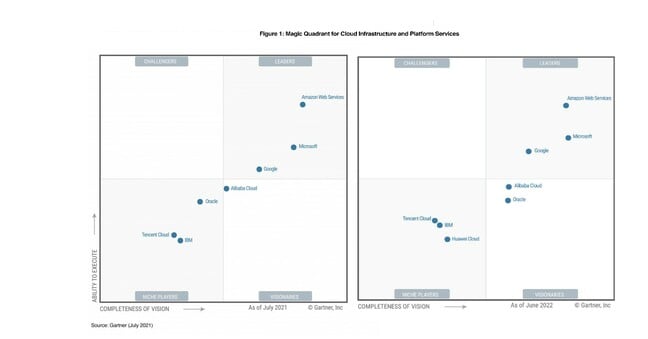
Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services 2021 and 2022 – Click to enlarge
Oracle’s breakthrough comes after Gartner analysts determined that Oracle was “innovating the market for new enterprise needs such as the sovereign cloud,” followed by “strict regulatory and data security mandated by law.” It is of particular value to customers in countries with privacy requirements.”
Microsoft uses its product licenses punitively against competing cloud providers.
“Oracle continues to deliver capabilities at an astounding year-over-year rate, close to the market leader in terms of hyperscale cloud capabilities. It will match or exceed, it’s a foreseeable future feature,” the document adds.
However, Gartner also knows that many customers have a strong dislike for Oracle, which they rate as a weakness.
“Oracle has a negative brand image for many organizations due to years of stringent compliance enforcement and inconsistent sales and support,” states the Magic Quadrant. “As a result, many companies resist the idea of using Oracle technology more than absolutely necessary.”
A weak partner ecosystem and lack of interest in non-Oracle workloads were also cited as weaknesses.
In the Leaders quadrant, AWS continues to lead in terms of market share, feature breadth, and ecosystem.
But Gartner warns that the cloud colossus is burning some customers to the ground.
“AWS often optimizes short-term transactions with customers, especially during contract renewals, resulting in customer relationship erosion,” the document states. “This paints a picture of the challenges ahead for AWS, with changes in management, shifting customer priorities, provider preferences in different regions, and a wealthy competition.”
Reliance on the us-east-1 region for operational and customer systems is cited as a weakness hampering AWS’s crisis response capabilities, while its weak multi-cloud and sovereign cloud strategy has also been criticized. .
Microsoft has been praised for its strong market share, industry solution availability, and hybrid and multi-cloud offerings.
Gartner allows exceptions to Microsoft’s licensing practices.
“Microsoft is punitive to competing cloud providers by making it more expensive to deploy Windows workloads outside of Azure, using licenses for their own products such as Windows and SQL Server,” Quadrant said. said. Azure has also been criticized for its opaque costs and struggling to innovate to address security and resilience issues.
Google was praised for its revenue growth, but was warned that it was still losing money. The advertising and search giant has also been criticized for raising prices after taking advantage of discounts to win over customers.
Oracle has a negative brand image due to years of strict compliance enforcement and inconsistent support.
Alibaba Cloud was recognized for its adoption in what Gartner called “China and the broader synosphere,” a market analysts believe the cloud should be considered. Gartner praised Alibaba Cloud’s partnerships with key software vendors such as SAP, Salesforce, IBM, and VMWare, but noted that it “has been more consistent, more transparent when it comes to discounts and pricing compared to international competitors. , or lack predictability.”
Gartner sometimes accuses IBM’s cloud of being unreliable and immature. Big Blue Cloud was recognized this year for its focus on regulated industries, modernization of workloads running on its own hardware, and the strength of Red Hat’s OpenShift container wrangling range.
But Gartner worries that IBM hasn’t put reliability issues behind it, developed solid sovereign cloud capabilities, and has yet to find a niche it can own.
“IBM Cloud has yet to find a competitive uniqueness compared to other providers in the market,” the document states. This is because we have not yet integrated legacy products into Red Hat’s and hybrid and multicloud offerings.
Tencent Cloud, which was in the same niche player spot as last year, also gained a spot in the Quadrant.
Gartner believes Gartner belongs there because it provides powerful tools for companies wanting to serve the Chinese consumer market and provides “rapid decision-making on exceptions and discounts for large customers.” .
Gartner, however, is concerned that Tencent is no longer interested in offering general-purpose workloads. China’s cloud has also been criticized for its slow pace of innovation. ®
[ad_2]
Source link
