[ad_1]
Sustainability in printing is becoming an increasing priority around the world, and print buyers are paying more attention to the carbon footprint of all their business activities. This can provide tangible commercial benefits for printing systems and operations that truly reduce their environmental impact. In this article, Smithers shares his latest insights on the short- and medium-term impact of greener printing initiatives.
John Nelson, Editor, Smithers
Sustainability in printing is becoming an increasing priority around the world, and print buyers are paying more attention to the carbon footprint of all their business activities. This can provide tangible commercial benefits for printing systems and operations that truly reduce their environmental impact.
As the industry faces 2023, rising energy prices in Europe are creating a new need for energy efficient printing. In this exclusive WhatTheyThink content, Smithers, a leading consulting firm in the paper, print and packaging industry, shares their latest insights on the short- and medium-term impact of greener printing initiatives.
low carbon digital production
Digital (electrophotographic and inkjet) OEMs are actively seeking to capitalize on the demand to reduce energy usage in their print rooms. In contrast to offset and flexographic printing, digital requires significantly less preparation, saving time, energy and ink. For analog printers, these are typically amortized over longer print runs, but print runs have trended downward since the pandemic, with shorter repeat orders being placed with faster turnarounds. The main reasons for this are tighter cash management by print buyers and a desire to reduce inventories, but such benefits can also be spun into improved sustainability, especially in reducing waste. I have.
In addition, inkjet presses continue to improve throughput rates, making them commercially viable at longer print runs, and now HP Indigo’s new LEPx-configured V12 presses offer similar potential to toner. I promise.
Analog OEMs are not blind to this trend and are increasingly adapting new automation and low energy equipment to their print lines. His one option for large scale converters is to recycle production line exhaust. Smaller converters may not have the same opportunities, but they can take smaller steps to reduce their energy usage.
A parallel trend is radiation curing operations that use a new generation of low-energy UV curing lamps to reduce energy use in curing stations.
There are competing claims as to which equipment and configurations delivered the greatest reductions in carbon input. Sustainability goals are now central to the corporate commitments of print buyers. This provides an objective, cost-effective way to track all factors in delivering a print job (energy, consumables, transportation/transportation, waste, etc.) in order to enable customers to choose a more environmentally friendly printing partner. There is growing interest in life cycle analysis as agreed in .
substrate
In the wider sustainability debate, a major driver is the replacement of plastics, especially single-use plastics, with more recyclable alternatives. This trend is especially noticeable in packaging, where packs and labels form real touchpoints, helping shoppers determine how serious a brand is about its commitment to the planet.
The impetus for printers is to manage the transition from plastic to paper without compromising print quality. On the press, this means it can handle heavier media and print effectively on uneven surfaces, supporting inkjet adoption. Many modern presses are built to handle heavier materials, including the kraft grades currently found in packs for customers.
This is because packaging is already a major growth target for most OEMs. Publication volumes continue to decline in North America, and the graphics/advertising outlook is clearly flat. By contrast, the region’s packaging work (excluding labels) is expected to be worth $99.25 billion in 2023, with real growth projected to be +2.1% y/y through 2027. increase(The future of digital vs. offset printing by 2027).
Recyclability has emerged as the most important metric for brand owners in packaging, giving new impetus to effective de-inking techniques. Failure to remove other components such as inks and coatings can compromise both the appearance and material strength of the reclaimed pulp. This will not only stimulate new R&D expenditures, but also move away from difficult-to-remove decorative effects such as metallic decorations and glitter. A vision of a circular economy for materials has led to a scrutiny of the migration of traditional publishing inks, especially mineral oil hydrocarbons, which pose potential health risks if recovered pulp is used in food contact. There is a possibility. In Europe, Germany has passed legislation specifically protecting this issue. In France, they are banned on packaging and, from January 1, 2023, on consumer advertising materials and catalogs.
water-based printing
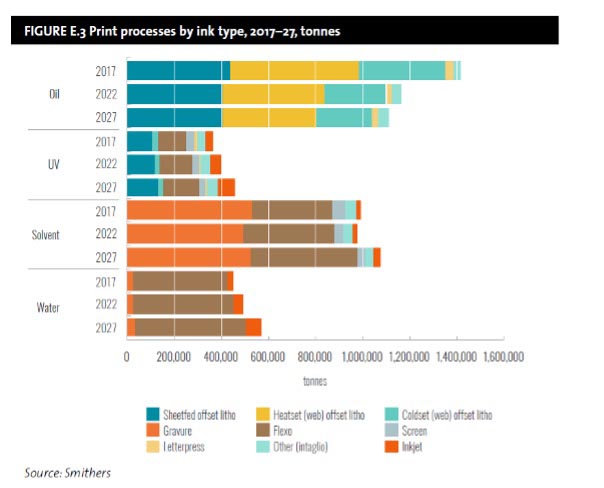
Another contribution ink companies are making is expanding the range of water-based (water-based) inks in their portfolio, especially as an alternative to solvent-based formulations. The main markets for water-based inks are flexographic and inkjet printers, with a smaller segment for gravure printers.
By 2022, a range of water-based inkjet systems have been demonstrated. This includes Ricoh’s upcoming proposal for commercial printing, the Pro Z75 B2 sheetfed press, and Xaar’s Aquinox printheads for ceramics, coding and marking, textile corrugated, and other packaging substrates. increase.
Smithers projects that sales of water-based inks will exceed $5 billion in 2022. The future of water-based and solvent printing by 2027, compared to $7.67 billion for solvent-based inks. The aquatic segment is projected to grow the fastest at +5.6% y-o-y by 2027 (value basis). On the other hand, sales of solvent ink increased by 1.3% year-on-year, below the market average.
The main factors slowing the transition to water-based inks are the established market for solvent printing on flexo packaging and the poor performance of water-based inks on polymer substrates used for flexible packaging. Developed markets are seeing some progress towards these products, especially as package converters move to more absorbent paper substrates.
Across all ink types, rising raw material costs are combined with moves to increase supply chain transparency, repatriating supplies where possible. As these post-pandemic supply chains mature, they can mitigate the damage of sourcing raw materials in less regulated countries and tackle other issues such as child labor exploitation.
Smithers publishes a complete suite of market reports covering all the traditional, digital and diverse high-growth segments of the printing industry. Its latest research—The future of water-based and solvent printing by 2027—Available now from Smithers.
John Nelson is an award-winning editor and journalist with Smithers’ market reporting and consulting business. Here he covers market and technology developments across multiple technical and commercial segments. Home and personal care, sustainability, packaging, printing, paper, nonwovens, rubber, tires and more.
[ad_2]
Source link
